Cyber Incident Response Plan (CIRP): Defining Procedures to Secure Your Organization's Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability
Cyber Incident Response Plan (CIRP): Defining Procedures to Secure Your Organization’s Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability
A Cyber Incident Response Plan (CIRP) is a detailed, documented set of procedures designed to guide an organization’s response to a cyber incident. A cyber incident can be any event that poses a threat to the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of an organization’s information systems and data.
CIRP outlines an organization’s steps to identify, contain, mitigate, and recover from a cyber incident. It includes protocols for reporting an incident, communication plans, identification of critical systems and data, and roles and responsibilities of individuals within the organization during the incident response process.
CIRPs are typically developed by cybersecurity professionals and IT personnel, with input from legal and executive teams. They are tested through simulations and drills to ensure their effectiveness in a real-world scenario.
Maximizing Cybersecurity Readiness: The Benefits of Developing a Comprehensive Cyber Incident Response Plan (CIRP)
A Cyber Incident Response Plan (CIRP) provides several benefits for organizations, including:
1. Minimizing the impact of cyber incidents: A CIRP outlines a clear and effective response plan, to mitigate the impact of cyber incidents on an organization’s information systems and data. This helps reduce downtime and financial losses resulting from the incident.
2. Enhancing preparedness: Developing a CIRP requires organizations to identify their critical assets, vulnerabilities, and potential threats. This helps increase their preparedness to prevent and respond to cyber incidents effectively.
3. Improving response time: A well-designed CIRP outlines specific roles, responsibilities, and communication protocols to ensure a timely and effective response to cyber incidents.
4. Demonstrating due diligence: Having a CIRP in place demonstrates an organization’s commitment to cybersecurity best practices and can help reduce legal and regulatory liabilities.
5. Enhancing stakeholder trust: An effective CIRP can help an organization maintain its reputation and enhance stakeholder trust by demonstrating a proactive approach to cybersecurity.
6. Meeting compliance requirements: Many industries and regulatory frameworks require organizations to have a CIRP. Developing and implementing a CIRP can help organizations meet these requirements and avoid potential penalties or fines.
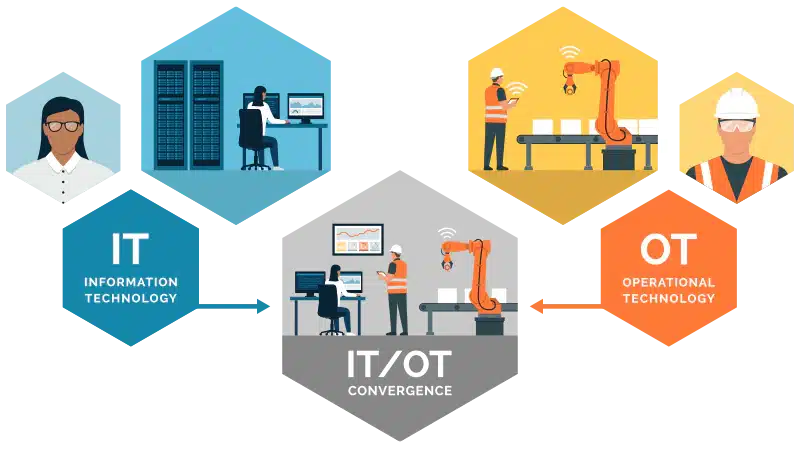
Understanding the Key Differences between IT and OT Cyber Incident Response Plans (CIRPs) for Effective Cybersecurity Management
IT (Information Technology) and OT (Operational Technology) Cyber Incident Response Plans (CIRPs) differ in their scope, focus, and objectives.
IT systems primarily manage organizational data and communications, while OT systems manage physical processes such as manufacturing, transportation, and energy production. As a result, IT and OT systems have different architectures, protocols, and security requirements, which affect their CIRPs.
The primary objective of an IT CIRP is to minimize the impact of a cyber incident on the organization’s information technology systems, networks, and data. In contrast, the primary objective of an OT CIRP is to minimize the impact of a cyber incident on the organization’s operational technology systems, including critical infrastructure such as power plants, transportation systems, and water treatment facilities.
Another key difference is the type of incidents they are designed to address. IT CIRP is designed to handle incidents that affect information systems, such as malware infections, data breaches, and denial-of-service attacks. OT CIRP is designed to handle incidents that affect physical processes, such as power outages, equipment malfunctions, and system failures.
The response teams responsible for IT and OT CIRP differ in their expertise and responsibilities. IT CIRP response teams typically comprise cybersecurity experts, network engineers, and IT professionals. In contrast, OT CIRP response teams include operational experts who are familiar with the organization’s physical processes and machinery.

In conclusion, a Cyber Incident Response Plan (CIRP) is a critical tool for any organization looking to minimize the impact of cyber incidents and enhance its cybersecurity readiness. A well-designed CIRP outlines a clear response plan, roles, and responsibilities, communication protocols, and testing and training procedures. Developing a CIRP not only demonstrates due diligence and compliance with regulatory requirements but also helps organizations maintain their reputation and enhance stakeholder trust. It is important to recognize the key differences between IT and OT CIRPs, which require different response teams, expertise, and protocols. Investing in a comprehensive CIRP can help organizations effectively prevent, detect, respond to, and recover from cyber incidents, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their information systems and data.


